reading-notes
Trees
Terms
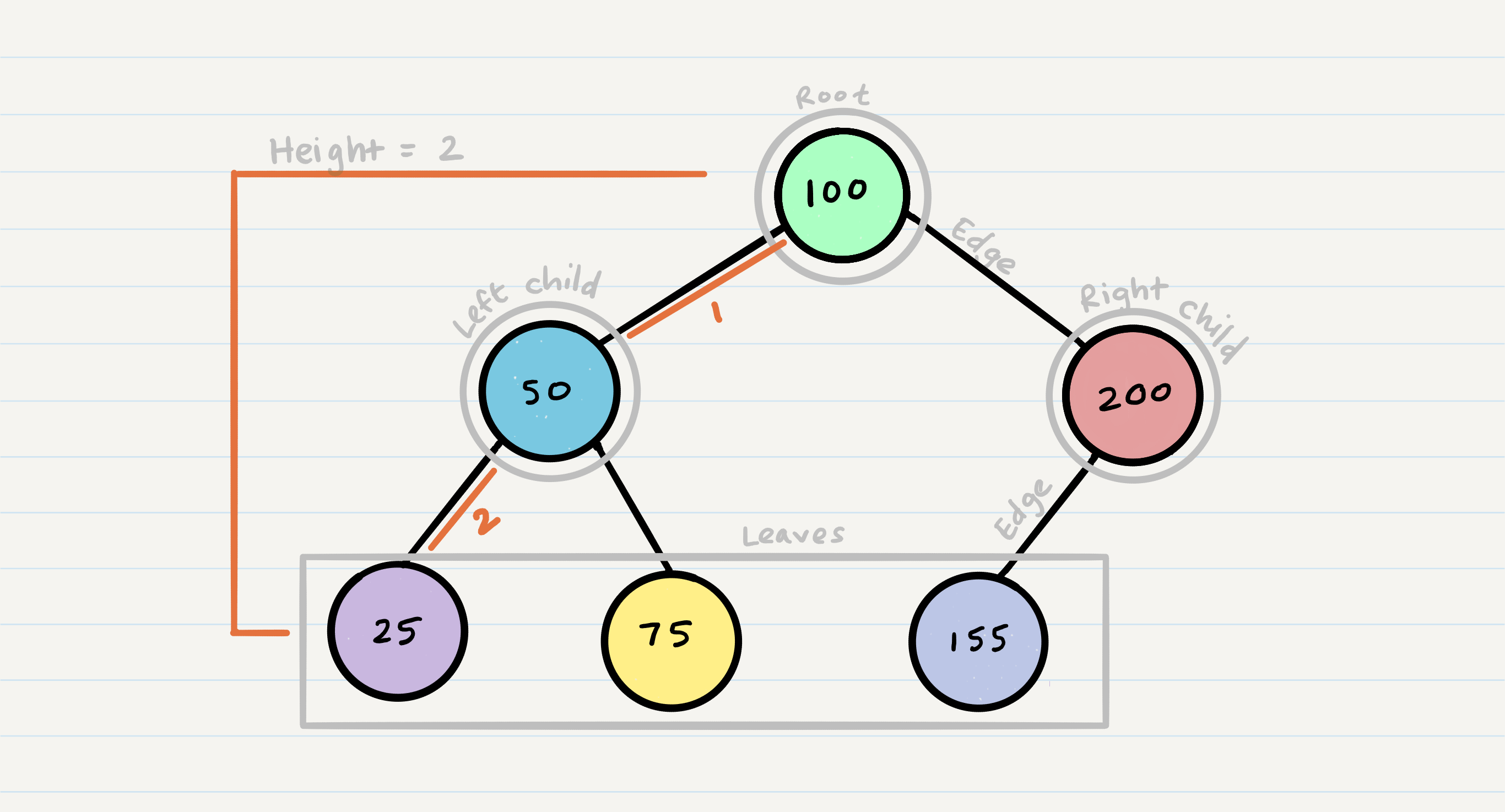
Node- Individual item in the treeRoot- First/top node in the treeLeft Child- Node positioned to left of a node or rootRight Child- Node positioned to right of a node or rootEdge- Link between parent and child nodeLeaf- Node that contains no childrenHeight- Number of edges from root to bottommost node
Traversing Depth First
Prioritze going depth (height) first.
Common to use recursion to search, using the call stack to navigate back up after the end
Types
Pre-order- root » left » right- Print root, then search down left recursively
- Once left is null, search down right recursively
- When a leaf is hit, we pick up the rest of the function call
ALGORITHM preOrder(root) // INPUT <-- root node // OUTPUT <-- pre-order output of tree node's values OUTPUT <-- root.value if root.left is not Null preOrder(root.left) if root.right is not NULL preOrder(root.right)-
In-order- left » root » rightALGORITHM inOrder(root) // INPUT <-- root node // OUTPUT <-- in-order output of tree node's values if root.left is not NULL inOrder(root.left) OUTPUT <-- root.value if root.right is not NULL inOrder(root.right) -
Post-order- left » right » rootALGORITHM postOrder(root) // INPUT <-- root node // OUTPUT <-- post-order output of tree node's values if root.left is not NULL postOrder(root.left) if root.right is not NULL postOrder(root.right) OUTPUT <-- root.value
Traversing Breadth First
Prioritze going breadth (width) first.
Traditionally uses a queue, instead of call stack/recursion
- Add root, A, to queue
- Dequeue node A to check it
- Enqueue left B and then right C
- B is now in front of queue
- Repeat!
- Dequeue B
- Enqueue D and E
ALGORITHM breadthFirst(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- front node of queue to console
Queue breadth <-- new Queue()
breadth.enqueue(root)
while breadth.peek()
node front = breadth.dequeue()
OUTPUT <-- front.value
if front.left is not NULL
breadth.enqueue(front.left)
if front.right is not NULL
breadth.enqueue(front.right)
Binary Trees
Trees with only two children per node.
No specific sorting order by definition
Adding - Typical to fill all child spots, but not required. This would use ‘breadth’ first traversal
Big O Time: Adding is O(n).
Big O Space: Breadth first, O(w) w=wdith
Binary Search Tree
Trees where all nodes smaller than root are on left, larger on right.
Searching: Traverse side based on comparison to n
Best approach is a while loop until you hit leaf or node you’re searching for
Big O Time: Adding is O(h), h=height
Big O Space: O(1)